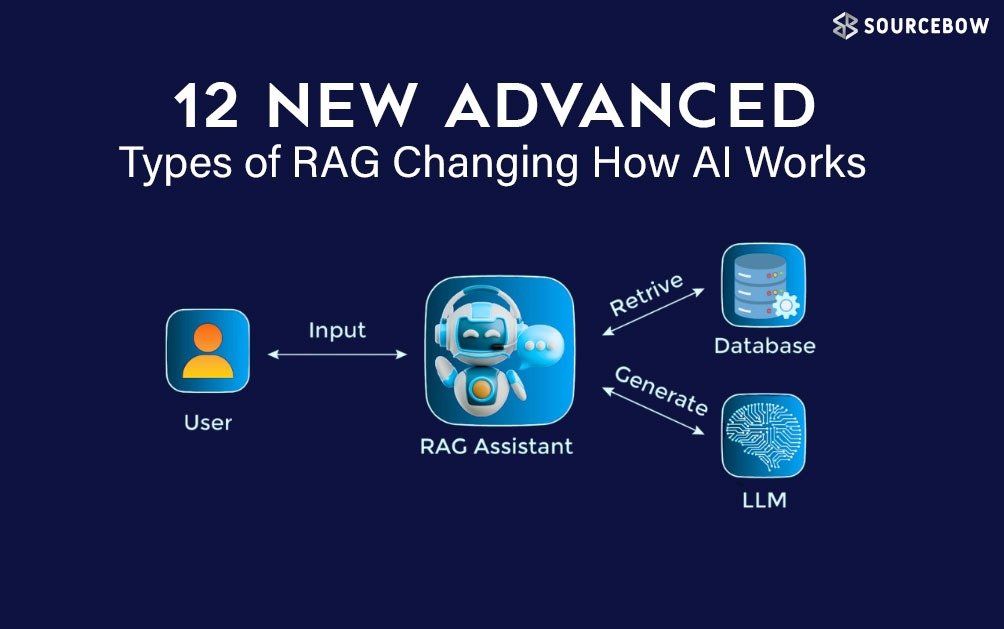
12 New Advanced Types of RAG That Are Quietly Changing How AI Really Works
RAG is no longer just a smart trick. It has grown into a full system design approach. What started as a simple way to fetch documents and generate answers has now turned into something much deeper. Systems today think, decide, retry, correct themselves, and even plan ahead before answering.
That shift happened because real problems are messy.
Users ask unclear questions. Data is scattered. Answers depend on context, timing, and sometimes previous mistakes. Traditional RAG struggles here. Advanced Types of RAG exist because one-size-fits-all pipelines simply do not survive real-world use.
Below are twelve advanced RAG types that are becoming more common in serious AI systems. Each one solves a specific pain point. Some feel subtle. Others completely change how the system behaves.
1. Agentic RAG as an Advanced RAG Pattern
Agentic RAG gives decision-making power to the system.
Instead of following a fixed pipeline, the model acts like an agent. It decides when to retrieve, where to retrieve from, and whether it needs more information before answering.
This is useful when the same query might need different data sources depending on intent. For example, a question about pricing could be informational or transactional. Agentic RAG pauses, thinks, and routes accordingly.
It feels less robotic and more intentional.
2. Routing Based RAG in Advanced RAG Systems
Routing RAG focuses on one simple idea. Not all data belongs in one place.
The system first understands the question, then routes it to the right retriever or knowledge base. Documentation queries go one way. Policy questions go another. Logs, FAQs, or structured tables go elsewhere.
This avoids noisy retrieval and improves accuracy without adding heavy logic. It is often the first step into advanced RAG thinking.
3. Multi Step Reasoning RAG for Complex Queries
Some questions are not questions. They are bundles of questions tied together.
Multi step reasoning RAG breaks a complex query into smaller parts. Each part is retrieved separately. The system then stitches everything together into one coherent response.
This is especially helpful for analytical, comparison-based, or multi-condition questions. Instead of guessing, the system builds the answer piece by piece. Slower, yes. But far more reliable.
4. Adaptive RAG as a Flexible Advanced RAG Type
Adaptive RAG reacts to what it sees.
If retrieval confidence is low, it retrieves again. If the answer feels incomplete, it refines the query. If the data source looks weak, it switches strategy.
This type of RAG does not assume the first attempt is correct. It adjusts mid-flight. It is useful when data quality is uneven or when queries vary wildly in clarity.
5. Self Reflective RAG for Better Accuracy
Self reflective RAG checks its own work.
After generating an answer, the system evaluates it. Did it answer the question fully. Is something missing. Does the reasoning make sense. If issues are found, the system retrieves again and improves the output.
This reduces hallucinations and shallow responses. It adds cost, but for high-stakes answers, it is worth it.
6. Corrective RAG in Advanced Retrieval Pipelines
Corrective RAG is focused on fixing mistakes rather than preventing them.
The system allows generation but watches for red flags. Inconsistencies, unsupported claims, or weak citations trigger correction loops. Instead of starting over, it patches the answer. This works well in environments where speed matters but accuracy cannot be ignored.
7. ReAct Based RAG for Reasoning and Action
ReAct RAG combines reasoning and action in a loop.
The system reasons about the problem, acts by retrieving or calling a tool, observes the result, then reasons again. This continues until the answer stabilizes.
It mirrors how humans solve problems. Think. Try. Adjust. Repeat. React RAG shines in tool-heavy systems and complex workflows.
8. Hierarchical RAG for Enterprise AI Systems
Hierarchical RAG introduces structure at the agent level.
Instead of one agent doing everything, there is a manager agent and several worker agents. The manager decides which agent should handle which part of the task.
This is powerful for enterprise systems where responsibilities are split across domains. It also makes debugging easier. Problems stay localized instead of spreading everywhere.
9. Multi Agent Collaborative RAG in Advanced Architectures
This is teamwork in AI form.
Multiple agents work together, each with a different role. One retrieves. One reasons. One verifies. One summarizes. They share context but operate independently.
The final answer benefits from multiple perspectives. It feels richer and more balanced, especially for complex or ambiguous queries.
10. Memory Augmented RAG for Long Term Context
Memory augmented RAG remembers past interactions.
The system stores previous queries, decisions, and outcomes. Future responses can use this memory to avoid repeating mistakes or to personalize answers.
This is useful in long-running sessions or user-facing assistants where continuity matters. The system stops feeling forgetful.
11. Tool Integrated RAG in Modern AI Workflows
Tool integrated RAG goes beyond documents.
The system can call APIs, run calculations, query databases, or trigger workflows during retrieval.
Instead of relying only on text, it uses live tools to fetch fresh or computed data.
This is essential for real-time systems like analytics, monitoring, or operations.
12. Hybrid Contextual RAG as the Most Advanced RAG Type
Hybrid contextual RAG mixes everything.
It blends static documents, dynamic tools, memory, agents, and adaptive logic into one system.
Context is not just text. It includes user history, environment signals, task state, and even system confidence.
This is where advanced RAG starts to feel like an intelligent assistant rather than a chatbot.
Why Advanced Types of RAG Exist at All
The reason is simple.
Real workflows are chaotic.
Questions change mid-way. Data updates constantly. Users do not phrase things cleanly. Systems need flexibility, not just speed.
Advanced RAG types exist to handle uncertainty. Each one tackles a different weakness of traditional pipelines.
Choosing the Right Advanced RAG Type
Not every system needs all twelve.
A small internal tool may only need routing RAG. A research assistant might benefit from multi step and reflective RAG. Enterprise platforms often combine hierarchical, adaptive, and tool-based RAG.
The trick is not complexity. It is alignment with the problem.
Final Thoughts on Advanced Types of RAG
RAG is no longer just retrieval plus generation.
It has evolved into a design philosophy. One that accepts mistakes, adapts to change, and thinks before answering.
Advanced RAG systems feel slower at times. But they are smarter where it matters.
As AI moves deeper into real workflows, these RAG types will not feel advanced anymore. They will feel necessary.
And once you build one properly, going back to a single pipeline feels almost impossible.